首语
- 之前立了个flag,LeetCode每天刷一道算法题,但随着算法题的深入,发现自己对数据结构的知识有些模糊。所以开始对数据结构的知识进行学习,记录的均是java版的数据结构和算法。2020年的第一篇博客从数据结构开始,第一节线性表(List)。首先是数据结构的相关概念。
数据结构
- 数据之间相互存在的一种或多种特定的关系的元素的集合!
逻辑结构
- 数据对象中数据元素之间的相互关系!
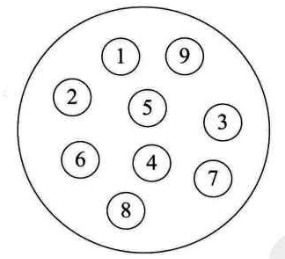
- 1.集合结构
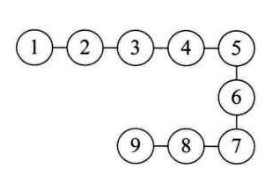
- 2.线性结构
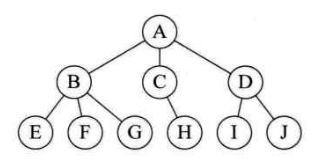
- 3.树形结构
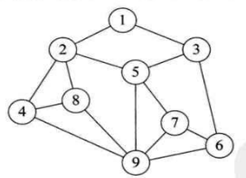
- 4.图形结构
物理结构
- 1.顺序存储结构
- 2.链式存储结构
数据类型
- 一组性质相同的值的集合及定义在此集合上的一些操作的总称!
抽象数据类型
- 一个数字模型及定义在该模型上的一组操作!
- 接下来进入线性表的学习
线性表(List)
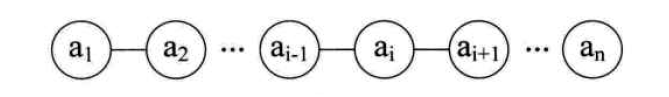
- a1是a2的前驱,ai+1是ai的后继,a1没有前驱,an没有后继。
- n为线性表的长度,若n=0时,线性表为空表。
顺序存储方式线性表
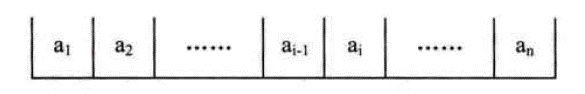
- 存储位置连续,可以很方便计算各个元素的地址。如每个元素占C个存储单元,那么有:
Loc(An)=Loc(An-1)+C,于是有:
Loc(An)=Loc(A1)+(i1)*C;
链式存储方式线性表
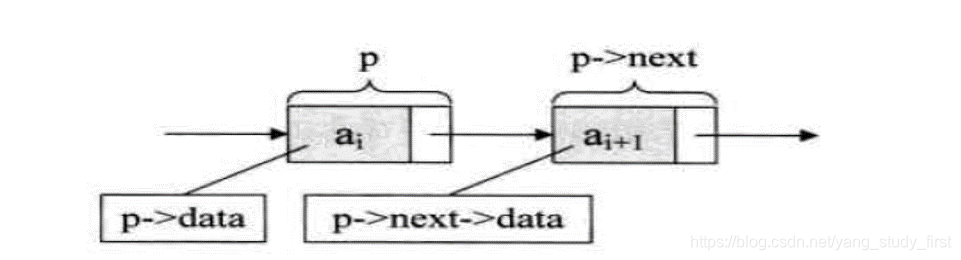
- 线性表的链式存储结构的特点是用一组任意的存储单元存储线性表的数据元素,这组存储单元可以是连续的,也可以是不连续的。
- 优点:插入和删除效率高。
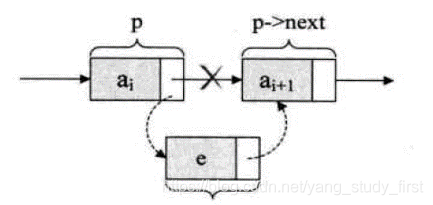
//插入
s->next=p->next
p->next=s;
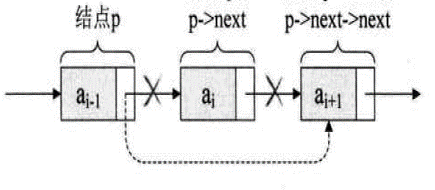
//删除
p->next=p->next->next;
- 缺点:查询效率低。
ArrayList源码
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this
* list. Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and
* any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their
* indices).
*
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return the element that was removed from the list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
return oldValue;
}
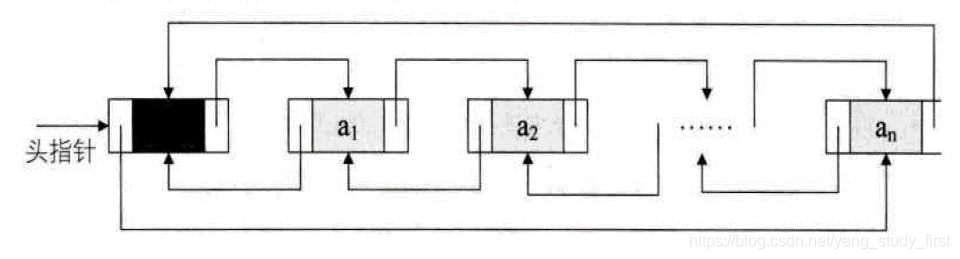
循环链表
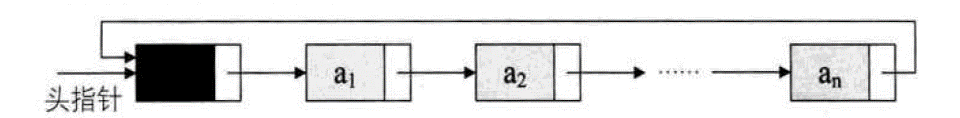
- 将单链表中终端结点的指针端由空指针改为指向头结点,就使整个单链表形成一个环,这种头尾相连的单链表称为单循环链表,简称循环链表。
双向循环链表
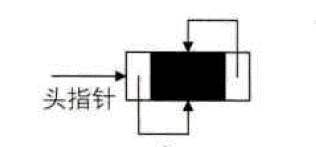
- 对于空的指针域
- 单向循环列表的每个结点中,再设置一个指向其前驱结点的指针域。
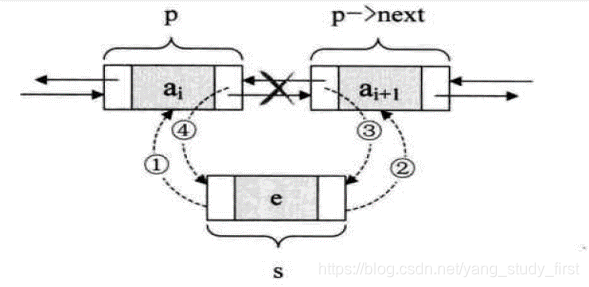
//双向循环链表的插入
s->prior=p;//把p赋值给s的前驱,如图1
s>next=p->next;//把p->next赋值给s的后继,如图2
p->next->prior=s;//把s赋值给p->next的前驱,如图3
p->nexts;//把s赋值给p的后继,如图4
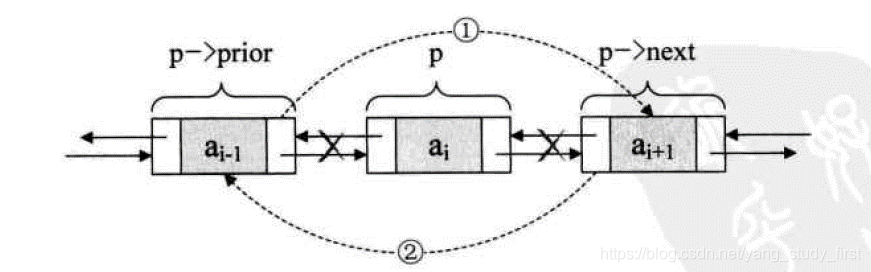
//双向循环链表的删除
p->prior->next=p->next;//把p->next赋值给p->prior的后继,如图1
p->next->prior=p->prior;//把p->prior赋值给p->next的前驱,如图2
LinkedList源码
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and any
* subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
if (index == size)
linkLast(element);
else
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
/**
* Links e as last element.
*/
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
/**
* Inserts element e before non-null Node succ.
*/
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {
// assert succ != null;
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this list. Shifts any
* subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their indices).
* Returns the element that was removed from the list.
*
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E remove(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return unlink(node(index));
}
/**
* Unlinks non-null node x.
*/
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
ArrayList与LinkedList
区别
1.ArrayList是实现了基于动态数组的数据结构,LinkedList是基于链表结构。
2.对于随机访问的get和set方法,ArrayList要优于LinkedList,因为LinkedList要移动指针。
3.对于新增和删除操作add和remove,LinkedList比较占优势,因为ArrayList要移动数据。
缺点
1.对ArrayList和LinkedList而言,在列表末尾增加一个元素所花的开销都是固定的。
对ArrayList而言,主要是在内部数组中增加一项,指向所添加的元素,偶尔可能会导致对数组重新进行分配;而对LinkedList而言,这个开销是 统一的,分配一个内部Entry对象。
2.在ArrayList集合中添加或者删除一个元素时,当前的列表所所有的元素都会被移动。而LinkedList集合中添加或者删除一个元素的开销是固定的。
3.LinkedList集合不支持 高效的随机随机访问(RandomAccess),因为可能产生二次项的行为。
4.ArrayList的空间浪费主要体现在在list列表的结尾预留一定的容量空间,而LinkedList的空间花费则体现在它的每一个元素都需要消耗相当的空间
应用场景
- ArrayList使用在查询比较多,但是插入和删除比较少的情况,而LinkedList用在查询比较少而插入删除比较多的情况。
LeetCode题例
/**
* author : yhj
* date : 2019/12/16
* desc :将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
* 示例:
* 输入:1->2->4, 1->3->4
* 输出:1->1->2->3->4->4
*/
public static class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int x) {
val = x;
}
}
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null) {
return l2;
}
if (l2 == null) {
return l1;
}
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2);
return l1;
} else {
l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next);
return l2;
}
}
/**
* author : yhj
* date : 2020/1/6
* desc :给定一个排序链表,删除所有重复的元素,使得每个元素只出现一次。
* 示例 1:
* 输入: 1->1->2
* 输出: 1->2
* 示例 2:
* 输入: 1->1->2->3->3
* 输出: 1->2->3
*/
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int x) {
val = x;
}
}
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
ListNode current = head;
while (current != null && current.next != null) {
if (current.next.val == current.val) {
current.next = current.next.next;
} else {
current = current.next;
}
}
return head;
}




